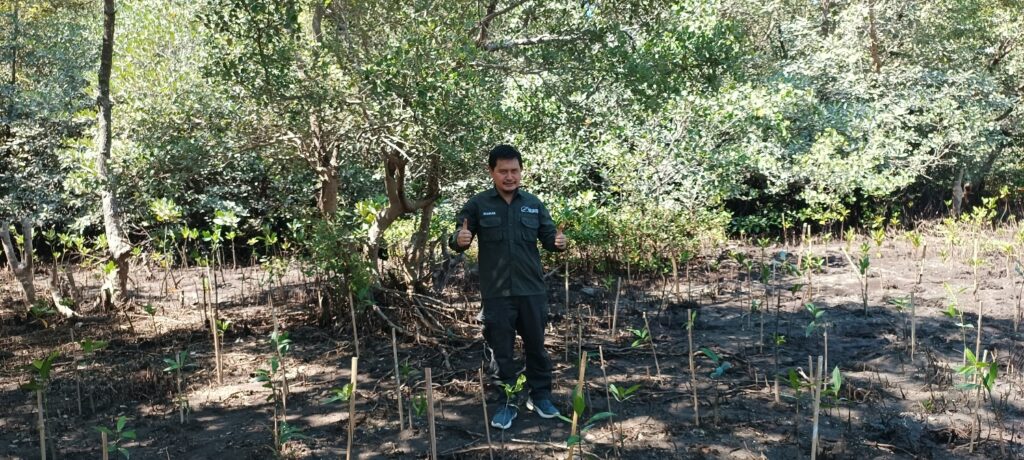
Connecting Forestry and Agriculture: Establishing a Forest Landowners Association in Puerto Rico
The Centro para la Conservación del Paisaje (CCP), a collaborator NGO of the Puerto Rico ISTF chapter is working on a linking strategy between the Puerto Rico Farm Bureau (Bureau) and the forestry sector. The objective is to integrate private forest landowners under the organized Bureau that has been working in Puerto Rico since 1924 and celebrated its centennial in 2024.
Historically, the Bureau has worked with farmers leaving agroforestry practices, like shaded coffee, in a gray area where landowners move according to funds’ availability and production objectives. The organization has arranged other agricultural sectors on the island such as milk production, honey production, meat sectors, etc. It has been an active and effective force of change toward policy reforms and is recognized as the voice of the farmers in the face of the government in Puerto Rico, the United States, and other countries. On the other side, the Department of Natural and Environmental Resources (DNER), the agency in charge of the technical assistance, management, and economic support programs for forestland owners, has kept a disconnection with agroforestry initiatives because it is considered a responsibility of the Department of Agriculture. As this “Accidental Adversaries” archetype identified in system dynamics modeling or system thinking analysis takes place in Puerto Rico; the island has increased its forest land cover, is under many programs focused on climate-smart practices, and is without a technical assistance program for private forest landowners.
The CCP met with the Bureau and discussed the agroforestry practices funded by climate-smart initiatives on the island and identified the need for technical capacity and a multilayered policy discussion. For example, shaded coffee is under a dilemma regarding using native vs. exotic species for shade as part of an incentivized climate-smart project. Agencies stare to the biodiversity priority, jumping the potential application of stand improvement practices that could manage a shade developed with exotic species toward a shade with native species. This situation identifies the gap in the information of silvicultural practices that could integrate the expected shade while providing the needed starting shade for the crop. The CCP has also expressed the needs and potential management options for forest landowners who are not farmers and need the technical assistance or representation to move forward with a review of the current programs and incentives related to forestry initiatives on the island.
The CCP is in the process of integrating a group of farmers to formally integrate the agroforestry and forest management sector under the Bureau to:
- Facilitate access to farmers to provide information and options to manage the forest resources.
- Provide an option to forest landowners to participate in the Bureau to receive information and discuss a review of the policies and programs that could consider environmental services incentives or other management options.
- Move a discussion with the U.S. Forest Service to examine and focus on forestry-related programs toward a more efficient strategy for the island.
The CCP concluded in 2024 with an agroforestry congress, which aimed to enhance the sector in the Bureau and improve the forest management options for an island with more forest coverage than active agriculture.
Note: This article was originally drafted in May 2024.
Author: Edgardo Gonzalez
Contact: edgonz581@gmail.com